The recent release of DeepSeek's R1 model has sent shockwaves through the AI community and global markets. While DeepSeek claims to have achieved this breakthrough with minimal resources, some experts and analysts are raising concerns about the company's rapid ascent and potential ties to the Chinese government. This report delves into the evidence and expert opinions surrounding DeepSeek, steelmanning the case that it may be a psychological operation (psyop) orchestrated by the Chinese Communist Party (CCP).
China's Pursuit of AI Dominance
China has explicitly stated its ambition to become a global leader in AI by 2030. This goal is driven by the recognition of AI's potential to transform industries, enhance national security, and elevate China's global standing. China aims to achieve a first-mover advantage in AI, allowing it to set the trend and lead the world in this critical technology. To achieve AI dominance, China is actively pursuing the following strategies:
Investing in AI research and development: China is promoting AI education and research programs to cultivate domestic talent and reduce reliance on foreign technology.
Developing domestic AI infrastructure: China is investing in advanced technologies like 5G networks and green data centers to support the deployment of high-capacity computing power essential for AI development.
Prioritizing AI applications across sectors: China is actively integrating AI into various industries, including healthcare, finance, and surveillance, to drive efficiency and innovation.
Monitoring global AI trends: China closely monitors global AI developments to identify opportunities for breakthroughs and strategically allocate resources to maintain a competitive edge.
DeepSeek's Suspicious Success
DeepSeek, a Chinese AI startup founded in 2023 by Liang Wenfeng, has rapidly gained attention for its advanced AI models, particularly the recently released R1 model. Liang, born in Guangdong in 1985, holds bachelor's and master's degrees in electronic and information engineering from Zhejiang University. He also runs a hedge fund, which could potentially be funding DeepSeek's operations.
DeepSeek's R1 model has demonstrated impressive performance on various benchmarks, rivaling and even surpassing established models from US tech giants like OpenAI and Google. DeepSeek claims that R1 offers performance on par with OpenAI's latest model and ranks among the top performers on the UC Berkeley-affiliated leaderboard called Chatbot Arena. However, DeepSeek's claims of achieving this breakthrough with limited resources and in a short timeframe have raised skepticism.
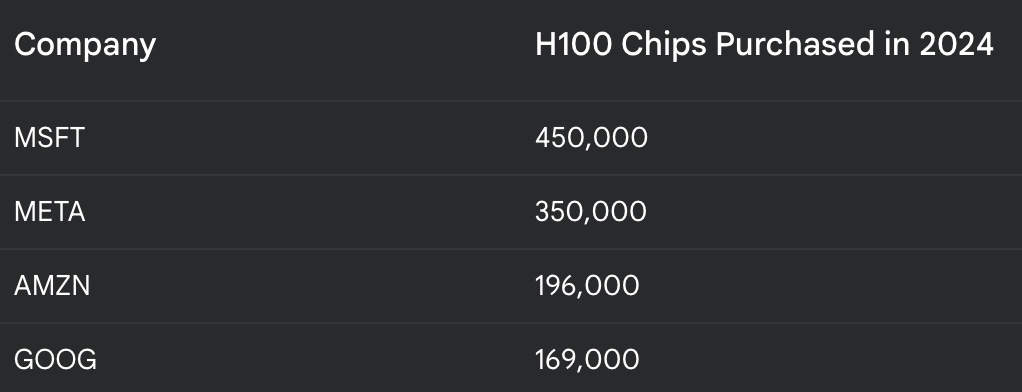
DeepSeek claims to have developed the R1 model in less than two years with only $5.6 million, using less advanced Nvidia H800 chips . This claim is particularly striking considering the significant investments made by US companies in AI development. For instance, the following table shows the number of H100 chips purchased by leading US tech companies in 2024 alone:
DeepSeek's approach challenges the traditional capital-intensive model of AI development. The company emphasizes research and employs an open-source strategy, potentially as a way to gain a competitive edge . DeepSeek also claims that it does not engage in external project cooperation or provide privatization deployment, which could be interpreted as a way to avoid scrutiny and maintain control over its technology.
DeepSeek's development timeline includes the release of DeepSeek Coder in November 2023, followed by DeepSeek LLM, DeepSeek V2, DeepSeek V3, and finally DeepSeek R1 in January 2025. The R1 model was trained using multi-stage training and large-scale reinforcement learning techniques. It employs a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture with 671 billion total parameters, but only 37 billion are activated per task. The training process involved curated datasets, R10-generated reasoning chains, and human preference alignment . A reward system was used during training, which included accuracy rewards and format rewards.
DeepSeek R1 has achieved impressive results on various benchmarks, including:
MATH 500: 97.3% accuracy
Codeforces: Ranked in the 96.3rd percentile
AIME 2024: 79.8% pass@1 score
MMLU: 90.8% accuracy
GPQA Diamond: 71.5% accuracy
SWE-bench Verified: 49.2% accuracy
AlpacaEval 2.0: Won 87.6% of evaluations
Despite these achievements, DeepSeek R1 has some limitations, such as mixing English and Chinese responses due to a lack of supervised fine-tuning.
Circumventing US Export Controls
Despite US export restrictions on high-end AI chips to China, evidence suggests that Chinese entities, including military and state-run research labs, have been acquiring Nvidia's A100 and H100 chips through various channels. These chips are crucial for developing advanced AI models, and their acquisition by Chinese entities despite the ban raises concerns about potential violations of export controls and possible government support for these activities.
One way Chinese companies are acquiring these chips is by establishing entities in nearby countries to purchase them before sending them to China . Another method involves smuggling the chips through various routes, including online platforms and physical markets. The availability of these chips in China despite the ban suggests that the US export controls may not be as effective as intended.
Evidence Suggesting a Psyop
The following points provide evidence that DeepSeek's rapid rise may be a calculated psyop by the CCP:
1. DeepSeek's Ties to the CCP: Reports indicate that DeepSeek's founder, Liang Wenfeng, has close ties to the CCP. This connection raises concerns about potential government influence, including access to resources, funding, and data not readily available to other companies.
2. Disruption of the US Stock Market: The release of DeepSeek R1 has erased $1 trillion in market cap from the US stock market, significantly impacting major tech companies like Nvidia, Microsoft, and Meta. This disruption aligns with China's strategic goals of challenging US dominance in the tech sector. By undermining investor confidence and creating a perception of China surpassing the US in AI innovation, DeepSeek could contribute to a shift in global AI leadership.
3. Disproportionate Benefits to Chinese Companies: DeepSeek's open-source strategy and low-cost models could disproportionately benefit Chinese companies. By providing affordable access to advanced AI technology, DeepSeek could accelerate AI adoption in China, giving Chinese companies a competitive edge in the global market. This strategy could also allow China to control the development and direction of AI technology globally, potentially setting standards and influencing the development of future AI applications.
4. Censorship and Control: Like other Chinese-made AI models, DeepSeek self-censors on topics deemed politically sensitive in China. For example, DeepSeek deflects questions about Tiananmen Square, President Xi Jinping, or the possibility of China invading Taiwan. This censorship aligns with the CCP's efforts to control information and maintain ideological dominance. DeepSeek's censorship could be a deliberate attempt to promote a specific narrative and limit access to information that contradicts the CCP's ideology.
5. Inconsistencies and Anomalies: DeepSeek claims to have developed R1 with limited resources and in a short timeframe. However, the company's rapid development and low cost raise questions about the feasibility of these claims. Some experts estimate that DeepSeek may have access to a larger number of Nvidia GPUs than it publicly acknowledges, further fueling suspicions about potential hidden resources and government support.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Threats
DeepSeek's rapid advancement and widespread adoption raise concerns about its potential use in cyberattacks and data privacy breaches. Its ability to process and analyze massive datasets in real-time makes it a formidable tool for identifying vulnerabilities in complex systems and supporting disinformation campaigns aimed at destabilizing US institutions.
DeepSeek could also be used in advanced persistent threats (APTs) for cyber-espionage, sifting through massive volumes of data to uncover sensitive intelligence. Furthermore, its potential use in cyber-surveillance campaigns raises significant ethical and privacy concerns, as it could be used to monitor online activity and collect personal data on a large scale.
A security flaw discovered in DeepSeek in December that could allow account takeovers adds another layer of concern. This vulnerability could either be a genuine flaw or a deliberate backdoor inserted by the CCP to gain unauthorized access to user data and systems.
Espionage and Intellectual Property Theft
China has a history of state-sponsored actors targeting US AI research and development to acquire algorithms, source code, and proprietary data. One well-known incident involved the alleged theft of autonomous vehicle technology at Apple by a Chinese-born engineer who downloaded large volumes of proprietary data before planning to relocate to a Chinese competitor.
DeepSeek's founder's close ties to the CCP raise concerns about potential access to the fruits of such espionage activities, potentially giving the company an unfair advantage in AI development.
Military Applications
China's focus on AI extends to its military applications, with the goal of achieving breakthroughs in core and critical technologies to protect its national security interests and create competitive advantages. DeepSeek's advanced AI capabilities could be leveraged for military purposes, potentially changing the military balance of power by providing China with overwhelming power in areas like intelligence gathering, autonomous weapons systems, and cyberwarfare.
Expert Opinions
Experts have expressed varying opinions on DeepSeek:
Supportive:
Yann LeCun (Meta's chief AI scientist): Acknowledged DeepSeek's success as an example of open-source models surpassing proprietary ones.
Skeptical:
Dr. Evelyn Hartman (AI policy researcher at the University of Cambridge): Raised concerns about DeepSeek escalating the AI arms race between global superpowers.
Neutral:
Analysts at Wedbush Securities: Believe that DeepSeek's model, while impressive, is not a significant threat to US tech dominance in the long run.
Vey-Sern Ling (managing director at Union Bancaire Privee): Highlighted DeepSeek's potential to disrupt the AI supply chain and challenge the investment case for high-cost AI infrastructure.
Potential Challenges and Limitations
Despite its impressive achievements, DeepSeek R1 faces several challenges and limitations:
Reliability Concerns: Being a new player in the global AI market, DeepSeek's reliability and long-term support may be questioned by businesses and developers.
Limitations in Handling Complex Tasks: DeepSeek's low-cost strategy could struggle with highly complex or resource-heavy tasks.
Potential for Misuse: Its open-source nature under the MIT license could lead to misuse or unethical applications.
Cultural Biases: Training on local or limited datasets might cause cultural or contextual biases, making it less effective globally.
Restrictions in Western Markets: Being a Chinese product, it may face restrictions or scrutiny in Western markets due to political tensions.
Lack of Partnerships and Integrations: Unlike OpenAI, DeepSeek lacks strong partnerships and platform integrations, which could limit its appeal to developers.
Competition with Established Giants: Competing with well-funded giants like OpenAI and Google could make it tough for DeepSeek to succeed outside China.
Synthesis
DeepSeek's rapid rise in the AI landscape has sparked both excitement and apprehension. While the company claims to have achieved remarkable breakthroughs with limited resources, several factors suggest a potential connection to the Chinese government and a possible psyop orchestrated by the CCP.
DeepSeek's founder's ties to the CCP, the company's suspicious claims of rapid development and low cost, and its censorship practices raise concerns about potential government influence and hidden agendas. The disruption of the US stock market following DeepSeek R1's release further aligns with China's strategic goals of challenging US dominance in the tech sector.
The potential implications of DeepSeek being a psyop by the CCP are far-reaching. It could lead to a shift in global AI leadership, accelerate China's technological advancement, and pose significant cybersecurity and data privacy threats. Moreover, DeepSeek's military applications could alter the military balance of power and further escalate tensions between China and the West.
While expert opinions on DeepSeek vary, it is crucial to consider the evidence and remain vigilant about the potential risks associated with this technology. Further investigation is needed to definitively confirm these suspicions and assess the long-term implications of DeepSeek's emergence on the global AI landscape.
If you don't already please follow @amuse on 𝕏 and subscribe to the Deep Dive podcast.






Similar and interesting take here: https://x.com/Cholly/status/1883789473445552308